1.Introduction
Traceroute is a tool that obtains a network route to destination nodes for an IP (Internet Protocol) network. Its feature is often used to check failure routers on network routes when a specific node does not communicate with ping. Traceroute utilizes TTL (Time To Live) for IP packets to achieve its feature. This article introduces how to utilize TTL for IP packets to obtain a network route.
2. Network-Layer
Packets pass through multiple networks and routes when we use the internet to communicate with distant destinations. The Internet is a huge network of interconnected multiple networks. These networks are ISPs(Internet Service Provider), data centers, and other networks of many various sizes. A router connects networks to each other to achieve communication between different networks.
There are IP and ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol) for major network-layer protocols to achieve the internet. IP defines packet format and communication methods. It assigns an IP address for each device and can communicate devices to each other on the same IP network. ICMP is a protocol that plays a supplementary role in helping IP functions. It notifies IP errors and controls messages.
3.TTL in An IP Header
There are two versions of IP: IPv4 and IPv6 In this section, I focus mainly on TTL for IPv4. However, IPv6 also contains a Hop Limit field which is similar to TTL for IPv4. In addition, The basis idea of obtaining a network route can be used for both IP versions.
An IPv4 packet consists of a header and data. The IPv4 header stores information for sending IP packets such as destination address, source address, and checksum. Among them, TTL is a necessary field to achieve traceroute. TTL is used to limit the lifetime of IP packets. Originally, it was assumed that time would be counted up in seconds increments and up to 255 seconds was allowed. Actually, it is used to count the network hops with each hop decrementing the values by one. If the value is zero, the packet was dropped and sent back a notification packet. Its mechanism prevents the packet from looping.
4.Obtaining a Network Route
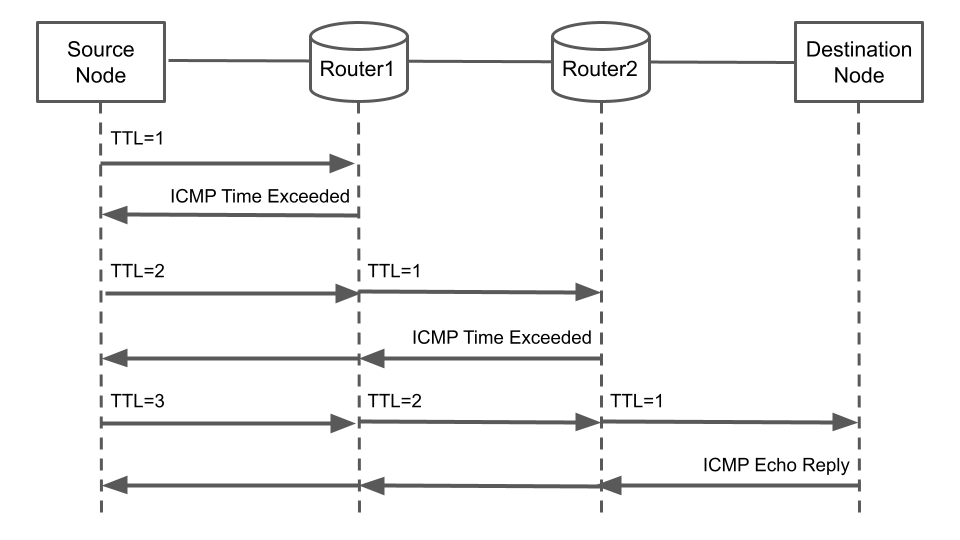
A useful idea for obtaining network routes is to send packets with adjusted TTL. Packets with adjusted TTLs that do not reach the destination are dropped by the routers on the network route. The router sends a notification message back to the source node. Therefore, the source node can obtain information about the router on the network route.
ICMP is used for notification messages. There is a message type of ICMP message called Time Exceeded. It type of message notifies the sender node that the TTL of the packet has reached zero and the packet was dropped.
Traceroute obtains network routes by utilizing them. It sends ICMP echo messages with incremented TTL and each router in turn replies with ICMP Time Exceeded messages. Then, traceroute receives these messages and checks the source address. Its process is repeated until an ICMP Reply message is received. The figure shows the flow of the process.
5.Implementation
Please see GitHub.
Simpleroute is a simple tool that outputs network routes. I implemented it using golang. It makes IP packets and ICMP packets myself and sends packets using raw socket and system calls (using syscall package). It sends packets with TTL incremented in a loop and receives ICMP packets to obtain network routes.
6.Conclusion
Traceroute obtains network routes utilizing TTL and ICMP Time Exceeded messages. It is a very simple idea, but useful.